From Luban Workshop to 'Silk Road' University, China trains professional personnel for Central Asia

"To have such a successful neighbor and not learn from them is like starving in a wheat field." This is how a Tajik scholar describes the desire of Central Asia to expand cooperation with China in the field of talent training.
From the professional construction of vocational education systems, to local teacher training, to cultivating the local social development need for talent ... In recent years, China and Central Asian countries in the cooperation of training professional personnel have been pressing the "accelerator button" under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Recently, Global Times reporters visited the "Silk Road" International University of Tourism and Cultural Heritage (Silk Road University) in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, and the Kazakh Luban Workshop project to see how China is helping Central Asia cultivate professional and technical talent, and building an important bridge for cultural exchange and mutual understanding between the two sides.
New university on ancient Silk Road
On September 2, the opening ceremony of the China-Uzbekistan Belt and Road International Laboratory, a joint archaeological and scientific laboratory for the technical protection of cultural heritage, was held at the Silk Road University. This was a major event that Zou Tongqian, the first Chinese vice president of the university, who came from Beijing International Studies University, attached great importance to.
The initiative to open the Silk Road University was proposed by Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev at the Shanghai Cooperation Organization Qingdao Summit in 2018. China has provided strong support for the establishment and construction of the university. For a long time, the university has closely cooperated with Chinese universities such as Beijing International Studies University and Northwest University.
In late August, Global Times reporters visited the Silk Road University and found that although the campus is not large, every detail is carefully arranged. On the walls of the main teaching building, there is a map of the ancient Silk Road and silhouettes of camel caravans, evoking the prosperity of the Silk Road in the past. In the corridor, there are paintings by students from various countries, depicting their understanding of the Silk Road.
Alysher Shamshidinov, a teacher at Silk Road University, told the Global Times that there are about 2,000 students at the university, mainly studying majors such as hotel management and logistics. It is worth mentioning that there are 85 international students, including 10 Chinese students pursuing master's degrees, as well as a number of renowned professors from world-famous universities.
In the past few years, China has played an important role in the construction of Silk Road University and the cultivation of local talent. In the library of Silk Road University, the Global Times saw a "China Corner" filled with Chinese books. In 2022, the Chinese Embassy in Uzbekistan donated more than 550 books and audiovisual materials in Chinese, English and Russian, covering topics such as Chinese culture, art, literature, history, tourism and Chinese language learning.
Since Zou took office as vice president in 2022, he and other Chinese colleagues have helped the university introduce a series of scientific research platforms, including the "One Belt and One Road" International Laboratory. They have also applied for the UNESCO Chair in Sustainable Heritage Tourism, invited globally renowned professors, and organized scholars from China, Central Asia, India, ASEAN and other countries and regions to conduct important research projects.
Cultivating more 'Lubans' of New Era
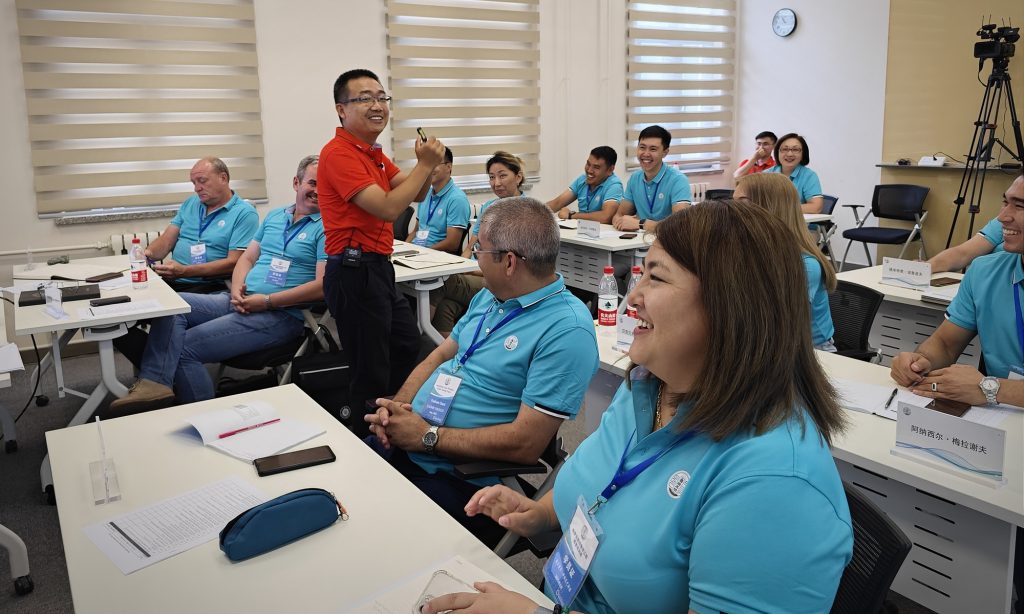
In August, during the summer vacation, the campus of Tianjin Vocational Institute is quiet and peaceful. However, one classroom is filled with lively discussions, sometimes interspersed with applause and laughter. In this classroom, 15 professional teachers from the East Kazakhstan Technical University (EKTU) are earnestly seeking advice from their Chinese counterparts on automotive repair techniques.
These foreigners are the first group of Kazakh teachers to come to China for training at the newly established Kazakh Luban Workshop. During the China-Central Asia Summit in May this year, Tianjin Municipality signed a cooperation agreement with East Kazakhstan Region to establish the Luban Workshop in Kazakhstan, officially launching the project.
"Can anyone tell me the different methods for replacing brake fluid in a car?" Guo Jianying, professor at the Automotive College of Tianjin Vocational Institute, vividly asked and demonstrated to the Kazakh teachers at the Luban Workshop how to replace brake fluid in a car. He also mentioned the management standards and procedures for waste oil in China. For this lesson, Guo prepared meticulously for a long time.
In the classroom, everyone eagerly raised their hands, expressing their opinions and engaging in lively interactions. They didn't even want to take a tea break. "We are very interested in the Luban Workshop training. Chinese teachers have a high level of expertise!" Murat Muzdybayev, a leading researcher at the School of Mechanical Engineering at EKTU, excitedly told the Global Times.
Muzdybayev noted that Kazakhstan has a great demand for automotive repair technicians, and they believe that the cooperation of the Luban Workshop, training equipment and resource sharing from China will greatly enhance the vocational training level of relevant majors at EKTU and promote the development of the local automotive repair industry.
The Luban Workshop is an international brand of vocational education created and led by Tianjin Municipality under the guidance of the Chinese Ministry of Education. It is named after Lu Ban, a legendary craftsman and inventor who lived 2,500 years ago in China. It combines academic education with vocational training, aiming to help countries along the BRI cultivate professional technical talent.
The Global Times learned that the specialties taught in the Luban Workshop are the most needed technologies for local industrial development, aiming to cultivate the most useful technical and skilled talent for local economic and social development.
Taking the Luban Workshop project in Kazakhstan as an example, Kazakhstan is a typical landlocked country with a high demand for land transportation. However, the country lacks a complete industrial chain in the automotive field, and there is a shortage of corresponding technical and skilled talent.
In recent years, the Kazakh government has also increased its new-energy vehicle (NEV) development plans, creating an urgent need for NEV maintenance technology and related talent. They hope to strengthen talent training in this area with China to "take the lead" in the field of NEVs, observers noted.
The curriculum of the Luban Workshop training for Kazakhstan has fully considered these factors. The training includes three modules: fuel vehicles, NEVs and intelligent connected vehicles, with a total of 20 training courses. During the training, the Tianjin Vocational Institute also arranges for teachers from EKTU to visit Chinese NEV and intelligent connected vehicle companies.
Samat Baigereyev, deputy dean of the School of Mechanical Engineering at EKTU, told the Global Times that the visit to Chinese car manufacturers such as Great Wall left a deep impression on him. He is very interested in China's technology in the field of NEVs and hopes to pass on these technologies to more Kazakh students.
Unlike many other international vocational training projects, in the Luban Workshop, Chinese teachers do not directly teach local students but train local teachers. Through such a flexible and down-to-earth form, the rich teaching resources, high-quality technical standards and more advanced experimental equipment in China's vocational education system can be more efficiently integrated into the national academic education system of the partner country in a more localized way.
Attractive talent training cooperation models
In recent years, China and Central Asian countries have witnessed rapid development in their cooperation in the field of talent cultivation, with the Luban Workshop and the Silk Road University serving as representative programs. At a recent seminar held in Beijing, Abdukhalil Gafurzoda, Director of the Centre for Friendship and Cooperation in Tajikistan expressed a strong interest in expanding cooperation with Chinese educational and research institutions, citing several key reasons.
First, Chinese universities are highly attractive to students from Central Asia, as Chinese diplomas are considered to be of high value. The number of Tajikistani students studying in Chinese universities has increased nearly 20 times in the past 15 years, reaching close to 4,000. This is not a coincidence, said Gafurzoda.
Second, the rapid expansion of economic cooperation between China and Central Asia in recent years has created a significant demand for local talent. Gafurzoda revealed that there are about 500 Chinese companies operating in Tajikistan, and Chinese enterprises have also participated in the implementation of 14 major investment projects in the country. Chinese investment accounted for 34 percent of Tajikistan's total foreign investment over the past decade.
"The establishment of the Luban Workshop in Dushanbe a year ago was, to some extent, aimed at addressing this issue," said the Tajikistani scholar.
With three projects already underway in Central Asia in Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan, where the Luban Workshop's talent cultivation standards and professional construction quality have gained wide recognition. Currently, 14 international professional teaching standards have been approved by the education ministries of cooperating countries and incorporated into their national education systems.
Why have the Luban Workshop and other personnel training cooperation projects?been able to make such good and fast progress in Central Asia?
"Our cooperation with another party does not come with any political conditions. We genuinely want to cooperate with Central Asian countries in the field of vocational education, help them improve their professional skills education level, and promote local industrial development. Through these collaborations, our teaching staff's capabilities and the internationalization level of our school can also be enhanced. It is a win-win situation," Meng Zheng, deputy director of the International Exchange Department of Tianjin Vocational Institute, told the Global Times.
Meng also noted that China's vocational education system is very complete and powerful, which includes technology, standards, resources, equipment and facilities,
"There are more than 1,300 vocational education institutions in China, and the improvement in scale and quality has been rapid. I believe that the level of vocational education in China is not inferior to internationally renowned vocational education models such as Germany and Australia. This creates a strong attraction for countries in Central Asia, including Kazakhstan," he said.